Speakeasies in the 1920s were secret bars that flourished during Prohibition when alcohol was banned in the United States. Prohibition lasted for thirteen years, from 1920 to 1933. Hidden behind unmarked doors, these venues offered an escape from restrictive laws and became hotbeds for jazz music and social change. Read on to discover how speakeasies in the 1920s shaped the Jazz Age and left a lasting mark on American culture.
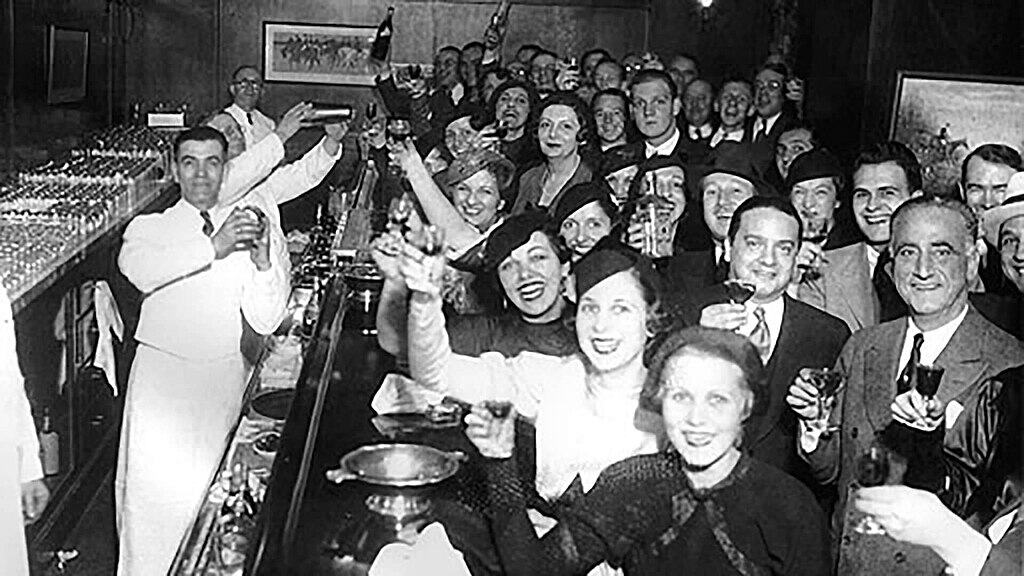
The enactment of Prohibition in 1920 led to the rise of speakeasies, secretive venues where people gathered to socialize and drink illegally. At the stroke of midnight on January 16th, 1920, the USA went dry due to the 18th Amendment. Prohibition led to hundreds of thousands of individuals losing their jobs as establishments like saloons and breweries were shut down. These hidden establishments not only provided a place to circumvent the law but also contributed to breaking down conservative social barriers of the time.
Speakeasies were central to the Jazz Age, serving as vibrant hubs for music and culture. By the mid-1920s, New York City had more than 32,000 speakeasies. They featured performances by legendary musicians like Louis Armstrong and Duke Ellington, helping to popularize jazz across the country. These venues also offered women new freedoms in social interactions and fashion, challenging traditional gender norms and encouraging greater independence.
Beyond their role as entertainment spaces, speakeasies fostered social integration and cultural diversity. Speakeasies were often hidden in basements, attics, and disguised as other businesses. They brought together people from different backgrounds, influencing social norms during the Prohibition era. The impact of these underground establishments can still be seen today in modern-day speakeasies, which celebrate their legacy with a nod to the past.

The Birth of Speakeasies
The 18th Amendment’s enactment in 1920 ushered in Prohibition in the United States, aiming to reduce alcohol consumption by banning the sale of intoxicating liquors. However, this law inadvertently led to the birth of numerous speakeasies—secret venues where people continued to enjoy drinks. Prohibition led to the establishment of tens of thousands of speakeasies across the nation. As legal alcohol sources were restricted to pharmacies for medicinal purposes, the high demand led to the proliferation of these hidden bars across the nation.
Initially makeshift saloons, speakeasies often required patrons to use passwords or codewords to gain entry and evade law enforcement. Every speakeasy had to have protections against raids, often including secret rooms and hidden exits. These illegal establishments became sanctuaries where people from different backgrounds gathered, breaking the era’s conservative social barriers. The term “speakeasy” became synonymous with these venues’ secretive and rebellious nature.
Speakeasies evolved beyond mere places to drink cocktails and enjoy bootleg booze; they became cultural hubs, with examples of jazz music, which existed before Prohibition, finding a new home in these venues, further cementing the connection between jazz and this era.
These underground clubs offered refuge from restrictive prohibition laws and played a key role in popularizing jazz and fostering a more integrated social environment.
The Jazz Age and Speakeasy Culture
Though jazz music predated Prohibition, the genre truly flourished during this era. The prohibition laws inadvertently created a thriving underground nightclub culture, with speakeasies at its core. The Jazz Age was characterized by a nationwide underground nightclub culture. These venues became the epicenters of the Jazz Age, filled with the sounds of jazz bands and patrons dancing the night away. Famous musicians like Louis Armstrong and Duke Ellington performed regularly in speakeasies, drawing large crowds and elevating jazz’s status.
Authors like F. Scott Fitzgerald immortalized the Jazz Age, capturing the essence of the era’s cultural and social dynamics. Speakeasies became symbols of the Roaring Twenties, defined by the exuberant mix of jazz music and liquor-infused partying. Flappers became the most visible heroines of the Jazz Age after women got the right to vote in 1920. Previously excluded from traditional saloons, women found a new sense of freedom in speakeasies. They embraced new fashion trends, like short skirts, and danced the Charleston, reflecting changing social norms.
Speakeasies offered a unique blend of music, dance, and social interaction, making them ideal venues for the cultural explosion of the 1920s. The roaring sound of jazz and the rebellious atmosphere of speakeasies embodied a defiance against conservative norms, making them a significant part of American history.
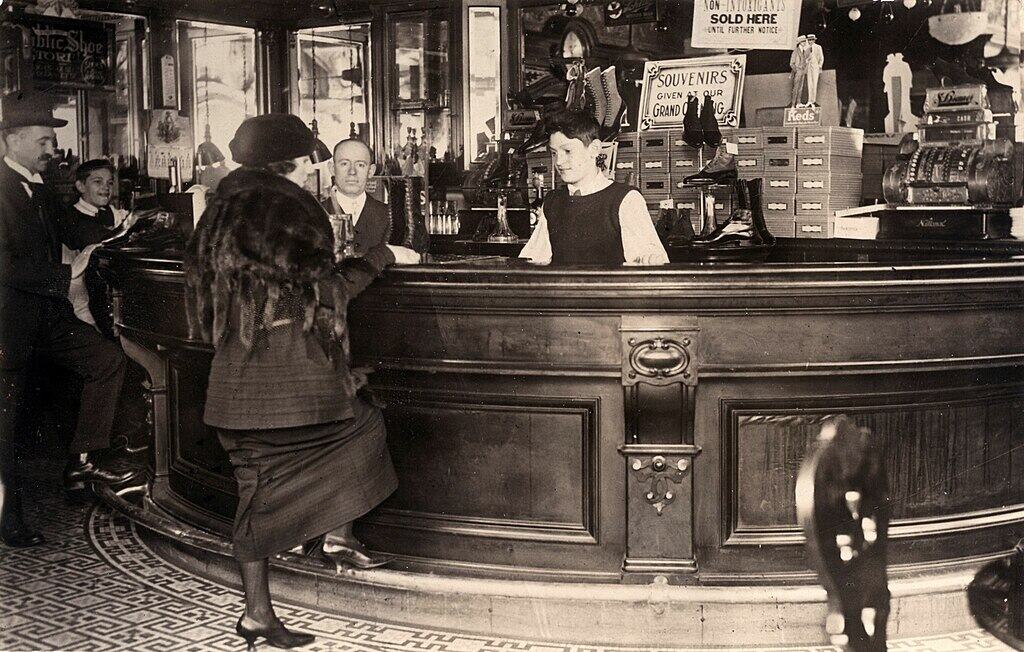

Inside the Speakeasy Experience
Entering a speakeasy felt like stepping into a different world, where patrons were greeted by the engaging sounds of laughter and jazz music. Customers often had to whisper their requests to avoid drawing attention from law enforcement, giving rise to the term “speakeasy.” The atmosphere was vibrant and intimate, with dim lighting and art deco decor creating a sense of mystery and exclusivity. Beyond serving alcohol, speakeasies featured live music and entertainment, becoming cultural hubs during Prohibition.
Speakeasies attracted a diverse clientele, including gangsters, politicians, and law enforcers, all seeking a place to socialize away from prying eyes. These venues offered camaraderie and excitement, where many speakeasies allowed people enjoyed bootleg liquor, danced to the latest jazz tunes, and experienced a taste of freedom in an otherwise restrictive era.
Key Figures in Jazz During Prohibition
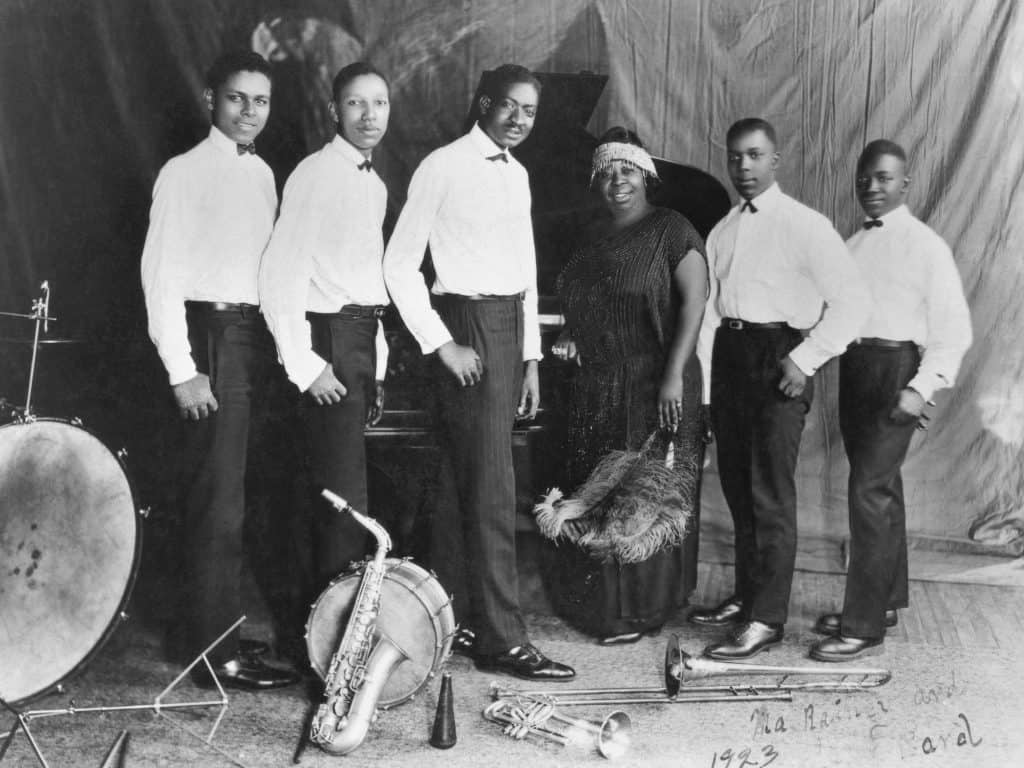
Prominent jazz musicians were instrumental in defining the sound and culture of speakeasies. Louis Armstrong, who moved from New Orleans to Chicago, shaped the era’s jazz sound with his innovative trumpet playing and charismatic stage presence. His performances in speakeasies popularized jazz and attracted large audiences.
Another significant figure, Duke Ellington, rose to fame in Harlem’s speakeasies, particularly at the Cotton Club. His sophisticated compositions and orchestral arrangements added a new level of elegance to jazz, making it an example of the speakeasy experience that prompted deep thought.
Female vocalists like Bessie Smith and Ma Rainey left a lasting impact by blending blues and jazz, creating a powerful and emotive sound that resonated with audiences.
Jelly Roll Morton, known for spreading early jazz, was prominent in the underground club scene. His contributions helped establish jazz as a dominant cultural force during Prohibition. Together, these musicians transformed speakeasies into vibrant cultural hubs that celebrated musical innovation and social diversity.
Jazz Music and Dancing
Jazz music, already popular before Prohibition, became a defining feature of speakeasy nightlife. Its improvisational nature allowed musicians to engage with audiences, creating a dynamic and interactive atmosphere. Patrons danced to lively beats, often losing themselves in the moment’s high spirits.
Speakeasy dance culture was lighthearted and carefree. People danced the Charleston and other lively dances, reflecting the era’s exuberance. Prominent jazz performers like Duke Ellington and Louis Armstrong, who performed at venues like the Cotton Club, further elevated jazz’s status in American music.
The blend of jazz music and dance created a unique and unforgettable experience for speakeasy patrons.
The Role of Women
Speakeasies significantly challenged traditional gender roles and provided women with newfound freedoms. These establishments welcomed women, offering them a space to drink, smoke, and socialize beyond traditional Victorian values. Women embraced a new social identity, enjoying previously frowned-upon activities like smoking and drinking.
Women’s presence in speakeasies also influenced fashion and lifestyle trends. Flappers became iconic in the Jazz Age with their bobbed hair and short skirts. Women in speakeasies defied societal expectations, expressing independence and control over their lives, much like the suffragettes. This cultural shift was significant in the broader social changes during the Prohibition era.

The Social Impact of Speakeasies
The vibrant atmosphere of speakeasies had a profound social impact during the Prohibition era. These establishments offered excitement and rebellion, drawing diverse crowds seeking entertainment and camaraderie. The intimate settings, often decorated with Art Deco influences and dim lighting created a lighthearted atmosphere that encouraged lively social interactions.
Speakeasies played a crucial role in breaking down racial and gender barriers. These venues challenged existing cultural norms and promoted a more inclusive social atmosphere by providing a space where people from different backgrounds could gather. The cultural rebellion symbolized by jazz and dancing in speakeasies was a powerful force influencing social customs during the Roaring Twenties.
The Jazz Age
Jazz music was the heartbeat of speakeasy culture, with its improvisational nature creating a vibrant and engaging environment. Musicians often played interactively with the audience, encouraging dancing and lively participation. The dynamic atmosphere of speakeasies was further enhanced by prominent jazz musicians, who drew large crowds with their performances.
The stock market crash of 1929 led to economic chaos, prompting many to seek affordable entertainment to escape their financial woes. Speakeasies became even more popular, offering controlled relief and enjoyment amidst the economic downturn, allowing patrons access to a world of enjoyment.
The enduring appeal of jazz music, with its ability to adapt and evolve, ensured it remained a dominant cultural force throughout the Jazz Age.
Breaking Social Barriers
Speakeasies were instrumental in challenging and breaking social barriers during the Prohibition era. These venues provided a space where individuals of different races and genders could interact freely, defying the segregation norms of the time. The inclusive atmosphere promoted a more integrated social environment, allowing men and women to socialize without societal constraints.
The cultural hubs created by speakeasies blended diverse communities, influencing social customs and norms during the Roaring Twenties. Speakeasies played a pivotal role in fostering social integration and challenging existing cultural norms by providing a space for diverse groups to gather.
The End of Prohibition
Rising public discontent with Prohibition laws and the economic chaos of the late 1920s contributed to overturning the 18th Amendment in 1933. The repeal marked the transition from illegal speakeasies to regulated bars, significantly reducing the number of speakeasies as they became legal drinking establishments. This transition also changed the jazz scene, with clubs becoming legitimate venues for performances.
The end of Prohibition marked a significant shift in American drinking culture. The underground speakeasy culture gave way to the rise of swing and big-band jazz in the late 1930s, reflecting the changing tastes and preferences of the time. The legacy of speakeasies, however, continued to influence American social and cultural life long after Prohibition ended.
Modern-Day Speakeasies
The charm of modern speakeasies lies in their ability to recreate the nostalgic experience of the 1920s. These contemporary establishments often feature secretive entrances and hidden bars, evoking a sense of exclusivity and mystery. Many modern speakeasies focus on craft cocktails, paying homage to the drinks of the Prohibition era.
Cities like San Francisco have embraced the speakeasy trend, with hidden, Prohibition-style bars that mirror the feel of the 1920s. These modern-day speakeasies offer patrons a chance to step back in time and experience the allure and excitement of the Jazz Age, complete with vintage decor and jazz performances.
The Lasting Legacy of Speakeasies
The journey through the world of speakeasies reveals a fascinating intersection of music, culture, and social change. From their secretive beginnings in response to Prohibition laws to their role in popularizing jazz and breaking social barriers, speakeasies left an indelible mark on American history. The vibrant atmosphere, diverse clientele, and cultural rebellion they embodied made them more than just illegal taverns; they were symbols of a dynamic and transformative era.
Frequently Asked Questions
How did jazz music become associated with speakeasies?
Jazz music became associated with speakeasies as these underground venues offered a platform for musicians to perform, solidifying jazz as a key form of entertainment during Prohibition.
What role did women play in speakeasy culture?
Women played a significant role in speakeasy culture by embracing newfound freedom to drink, smoke, and socialize, thereby challenging traditional gender norms. This environment allowed them to explore their identities beyond societal constraints.
How did speakeasies contribute to breaking social barriers?
Speakeasies facilitated social integration by allowing individuals of different races and genders to interact freely, challenging the prevailing segregation norms. This contributed significantly to the breaking down of social barriers during that era.
What is the legacy of speakeasies today?
Today’s legacy of speakeasies is reflected in modern establishments that embody the 1920s ambiance, featuring hidden entrances, vintage decor, and live jazz music, thus preserving the spirit of this iconic era.